Bariatric
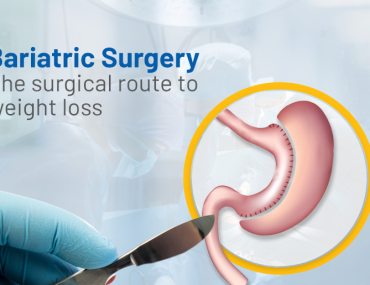
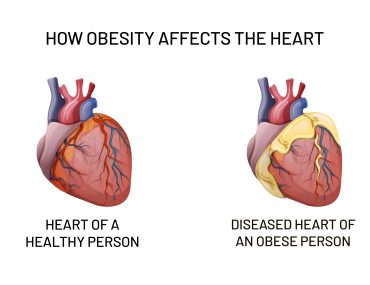
If you’ve tried every possible diet and exercised more than you ever could imagine but you’re still not losing any weight then considering bariatric surgery to treat your obesity-related condition could be a fair option. Because, obesity is a serious health condition that is directly linked to a list of chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, heart diseases, high blood pressure, osteoporosis, stroke, etc. And, bariatric surgery is a kind of surgical procedure that aids in weight loss by making changes to your digestive system. This surgery leads to weight loss by reducing the quantity of food your stomach can hold, causing you to feel full in a lesser quantity of food uptake. A person is considered obese and may require bariatric surgery only when his/her body mass index (BMI) falls under the high range of class 3 i.e. above 40.
Body mass index (BMI) is a measure of body fat based on height and weight that applies to adult men and women. The higher the BMI higher is the chances of a person to be affected by chronic diseases. Today, almost all bariatric surgical procedures are performed using minimally invasive techniques with a focus on fast recoveries. Most patients are sent home immediately the next day of the surgery and are expected to recover in two to three weeks.
There are various types of bariatric surgeries that a doctor may suggest to an individual depending upon the severity of the condition. Some common types are Gastric Bypass, Sleeve Gastrectomy, Adjustable Gastric Band, and Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch. Each of the surgery types has pros and cons and various patient factors affect which procedure is chosen including body mass index, eating habits, other health issues, and previous stomach surgeries. However, bariatric surgeries may not be suitable for everyone and it is always advisable to speak to your surgeon and try all other available alternatives before opting for weight-loss surgery.