The term cancer can be overwhelming for the majority of people. It can be physically as well as emotionally too much to take in for an individual along with people around them. Hence understanding cancer is very important because having the right information can lead to taking steps at the right time to cut down your risk of cancer. Cancer is a name given to a collection of diseases that are related. It causes body cells to divide rapidly and in some cases can also affect the surrounding tissues. The rapid creation of abnormal cells that grow beyond their boundaries is one of the most defining features of cancer, which can then invade other parts of the body; this process is referred to as Metastasis. The primary cause of death in cancer is Metastases.
Due to advanced technology and medicine, the treatments are constantly improving. With proper diagnosis and treatment, many cancers have a high cure rate. Between 30-50 % of cancer cases can be prevented by avoiding the risk factors and implementing existing prevention strategies.
Cancer is the leading cause of death in the world. After breast cancer, Lung cancer is the second most common type of cancer in the world. It is also one of the most common causes of cancer death in the year 2020. According to World Health organization Statistics, there were 2.21 million cases in 2020 worldwide in which there was 1.80 million death.
What is Lung cancer?
The two sponge-like organs in the chest are called lungs. The right lung has three sections called upper, middle, and lower lobes. The left lung has two lobes upper and lower lobes, left lung is smaller because the heart takes up more space on that side of the body. When we breathe, through the trachea (windpipe) the air inhaled goes into the lungs. The Trachea divides into tubes called Bronchi, which enters the lungs and is further divided into smaller Bronchi called Bronchioles. At the end of the Bronchioles, there are tiny sacs called alveoli. The main function of Alveoli is absorbing oxygen into the blood and removing carbon dioxide from the blood when you exhale.
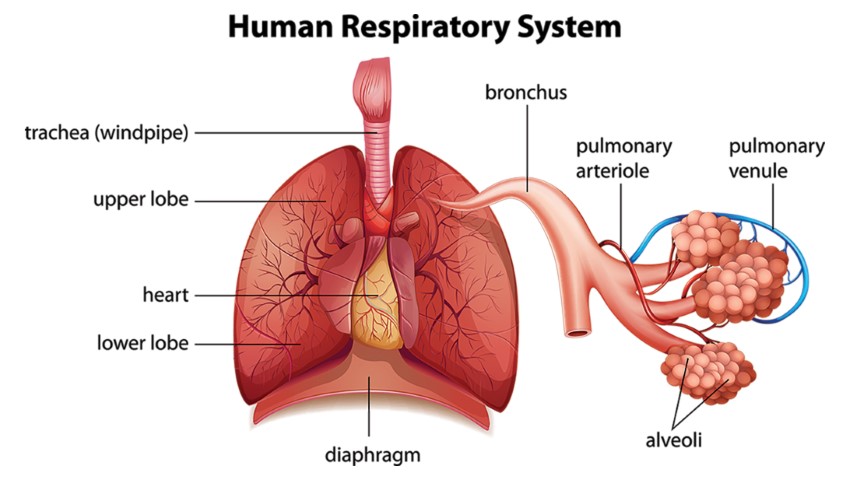


Lung cancer can start in any part of the lungs or airways which includes the windpipe the main airway or the lungs themselves. When there is an uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells inside one or both lungs the cells grow to form a tumor.
The major risk factor for lung cancer is smoking though not everyone who develops lung cancer has a history of smoking. Lung cancer can be fatal but with proper diagnosis and treatment, the outlook to it could differ.
Types of Lung cancer
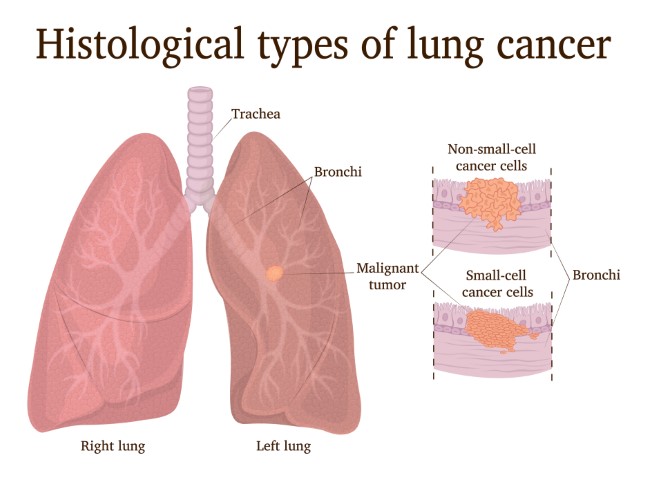
Cancer that starts growing in the lungs is called primary lung cancer. If cancer spreads from other parts of your body to the lungs is called Secondary lung cancer.
There are 2 types of Primary lung cancer:
- Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Small cell lung cancer
Small cell lung cancer is a fast-growing and more aggressive form of lung cancer. Cancer grows and spreads rapidly traveling to other parts of the body or metastasize more easily. Due to this, the condition is usually diagnosed after cancer has spread throughout the body, making recovery doubtful. But if it is detected in an early stage it may be treated effectively before cancer spreads.
Symptoms for Small cell lung cancer
SCLC is usually asymptomatic which means it doesn’t show symptoms. Once there are visible symptoms it often indicates that cancer has started growing and has infected other parts of the body.
Symptoms are:
- Wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Bloody mucus for the lungs
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- A persistent cough
If you notice any symptom connect to a doctor immediately.
Non-small cell lung cancer
It is the most common and less aggressive than Small cell lung cancer which means it doesn’t spread and grow rapidly.
NSCLC can be treated successfully with surgery, chemotherapy, and other treatments.
Smoking is the leading cause of NSCLC and other types of cancer.
Symptoms for Non-small cell lung cancer
- Hoariness
- Fatigue
- Coughing up phlegm or mucus
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Cough
You need to note that some of these symptoms may occur due to other reasons as well.


Risk factors for lung cancer
Anything that increases a person’s chance of getting cancer is classified as a risk factor. Some risk factors can be changed like smoking, but others like family history or a person’s age cannot be changed.
Some of the risk factors are:
- Smoking- Smoking remains the number one reason for developing lung cancer. The longer you smoke greater the risk.
- Passive smoking: If you are a non-smoker who hangs out with people who smoke, you are still at risk of developing lung cancer.
- Air pollution: Air pollution raises the risk of lung cancer especially in cities.
- Personal or family history: If you had relatives who suffered from lung cancer then the probability of you developing it increases.
- Exposure to Radon: A naturally occurring radioactive gas that results from the breakdown of uranium in soil and rocks is Radon. Breathing it in can expose you to a small amount of radiation.
We should be careful and consider all these risk factors to reduce the chances of developing lung cancer.
Coping with a cancer diagnosis can be stressful and difficult. Learn about your condition and treatment by talking to your doctor about it. Online resources can also be useful to understand and gain a sense of control over the situation.
Lung cancer can be fatal but early diagnosis often have a good chance of survival. People who are at high risk of developing lung cancer should consider getting regular screenings. People who are concerned with the risk factor should talk to a healthcare professional.