Cancer occurs when the cells in our body grow and multiply uncontrollably, and as the name suggests, blood cancer begins at the blood cells and bone marrow, where blood is produced. Stem cells in the bone marrow develop into three types of blood cells; red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Blood cancer occurs when abnormal blood cells start multiplying uncontrollably, thus affecting the functioning of the normal blood cells. Blood cancer is also known as hematologic cancer. This hinders the body’s ability to combat infections and prevents the production of new blood cells. There are three major types of blood cancer; namely –
- Leukaemia
- Lymphoma
- Myeloma
Let us look at these three types of blood cancer in detail.
Leukaemia:
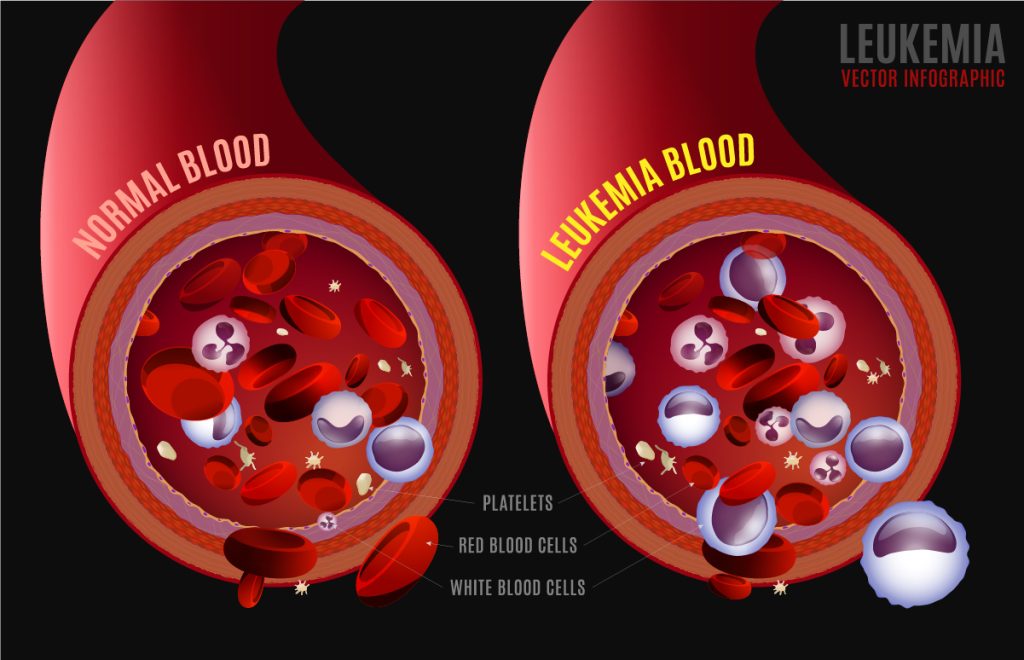


This type of cancer is found in the blood and bone marrow. There is a rapid production of abnormal white blood cells in those diagnosed with leukaemia. Due to the higher number of abnormal white blood cells, the body cannot fight infections. This also interferes with the bone marrow’s ability to produce more red blood cells and platelets. Leukaemia is divided into four types based on the kind of blood cell it affects and how quickly it grows.
Acute Lymphocytic Leukaemia (ALL): This type starts with white blood cells known as lymphocytes. In this condition, the body produces too many lymphocytes that interfere with the healthy white blood cells, preventing them from functioning effectively. This cancer is most likely to develop in children 3 – 5 years old or adults over the age of 75. Some of the risk factors include:
- A sibling diagnosed with Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
- Previous cancer treatment with chemotherapy or radiation therapy
- Increased exposure to radiation
- Genetic disorders such as Down Syndrome
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) begins at the myeloid cells that grow into white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. This condition leads to a decrease in the number of healthy blood cells. Acute Myeloid Leukemia mainly affects people over 65 and is more common in men. The risk factors of AML include:
- Previous treatment with chemotherapy or radiation therapy
- Exposure to toxic chemicals such as Benzene
- Smoking
- Prior history of blood disorders such as myelodysplasia
- Genetic conditions like Down Syndrome
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): This condition starts from the lymphocytes, just like ALL, but grows slowly. One may not notice any symptoms during the initial stages of cancer. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia affects people above the age of 70.
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): This type of blood cancer starts in the myeloid cells and grows slowly. This condition is more common in men as compared to women.
Lymphoma:
This type of blood cancer affects the lymphatic system, including the lymph nodes, spleen and thymus gland. The lymphatic system removes excess fluids from the body and produces immune cells. The white blood cells that help fight infections as known as lymphocytes. Lymphoma causes these cells to multiply, hindering the immune system from functioning effectively. The different types of lymphomas are:
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: Hodgkin’s Disease, this type of blood cancer starts in immune cells called the B Lymphocytes. The lymphocytes grow out of control, causing the lymph nodes to swell. This impairs the function of the immune system. In this, you can detect the presence of a specific type of cell known as the Reed-Sternberg cell.
Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: This type of cancer too begins at the lymphatic system and interferes with the functioning of the immune system. However, there is no presence of the Reed-Sternberg cell.
Myeloma:
This cancer develops in the plasma cells in the bone marrow. Plasma cells are a type of white blood cell responsible for making antibodies. Myeloma can cause damage to the bones and interfere with the healthy blood cells as they multiply, resulting the less production of antibodies to fight infections. This is very common in men over the age of 50. The risk factors of Myeloma include:
- Family history of Myeloma
- Obesity
- Exposure to radiation
What are the symptoms of Blood Cancer?
Some of the most common symptoms of blood cancer include:
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Sudden weight loss
- Excessive sweating at night
- Headache
- Breathlessness
- Discomfort in the abdomen
- Swollen lymph nodes
How is blood cancer diagnosed?
Your doctor will begin the diagnosis of blood cancer with a physical examination. Your doctor will also review your medical history, examine the lymph nodes, check for infections. Depending on the deductions of the physical exam, different types of diagnostic tests will be recommended.
Biopsy: In this test, a sample of your cell is collected for examination in a laboratory. For a particular type of blood cancer such as lymphoma, the doctors take a lymph node biopsy containing a lymph tissue sample or an entire lymph node.
Imaging Scans: Imaging tools such as CT scan, MRI, PET scan, and ultrasound can help stop tumours or an enlarged cell that may point to cancer. These scans are more effective for some types of blood cancer, such as lymphoma, than Leukemia that does not cause visible tumours.
Blood Tests: Blood tests measure the level of certain substances in your blood. For example, unusual levels of specific proteins may point to a health condition. A Complete Blood Count gives a cell count of different blood cells such as red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. The treatment for blood cancer depends on the type of cancer and how fast it progresses. While there are several treatment options such as stem cell transplantation, chemotherapy and radiation therapy, it is essential to ensure that you take certain precautions to prevent the disease by avoiding exposure to radiation, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy diet. If you notice any symptoms, talk to your doctor right away to diagnose the condition. Remember, early detection saves lives!




Comments are closed.