Introduction
Bariatric Surgery, for all good reasons, has been in increasing demand as an effective weight reduction alternative by people struggling to lose those extra pounds through non-surgical methods without any positive outcome. When at the peak of one’s weight, apart from the social, emotional, and physical embarrassment, the cardiovascular risks weighing on these obese people are the real cause of concern. One of the studies conducted by the American College of Cardiology reviewed the role of Bariatric Surgery in lowering CV risks in obese and suggested that it significantly lowered CV mortality and reduced heart failure, myocardial infarction, and stroke incidences.
Weight Loss Surgery or not, is always a difficult decision to make for people trying to lose weight. However, when no non-surgical treatment works, people often resort to this surgery as their final call.
In this blog, let us explore the connection between Bariatric Surgery and cardiovascular risks. For this, we need to understand how this treatment works and affects the cardiovascular health outcomes in a patient.
Understanding Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric Surgery treats obesity. But many of us feed on the misconception that surgery removes fat from your body. No, it does not. The surgery aims to reduce the size of your stomach and re-route the intestine track to restrict the food intake and the body’s ability to absorb nutrients. The smaller the stomach size, the fuller one feels with less food. The re-routing of the digestive tract limits digestion and absorption of the nutrients. Thus, it leads to considerable weight loss in a shorter span, when combined with proper diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
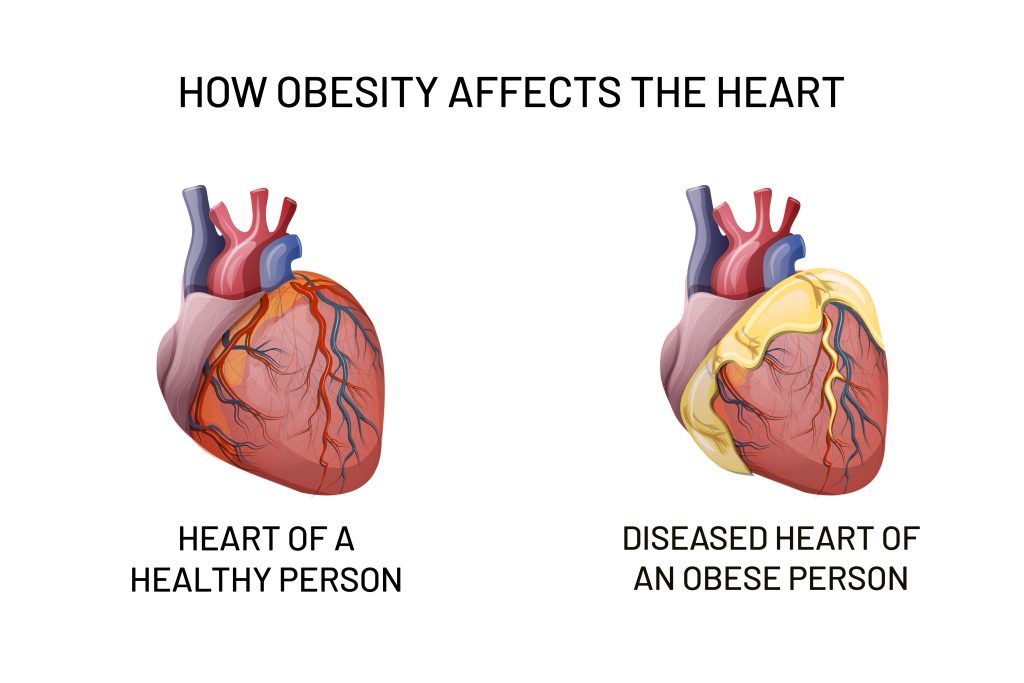
Obesity is the Root Cause of Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs).
Obesity is an excessive or abnormal accumulation of fat in the body that risks one’s health. It is a chronic and complex medical condition and has become common in people of all ages. It is the root cause of CVDs, often leading to death if left unaddressed. Obese are at a high risk of developing various heart-related issues like-
- High Cholesterol – A high amount of fat in the body causes blockages in the blood vessels, increasing the chances of stroke or heart attack.
- Type 2 Diabetes- Excessive storage of fat results in the muscles and tissues becoming more resistant to insulin, leading to the risk of developing type-2 diabetes. This impairs the circulatory, immune, and nervous system and leads to stroke or heart attack.
- High blood pressure- The amount of pressure the blood flow exerts on the inner walls of the arteries increases with the accumulation of fatty tissue. The heart needs to work hard to pump blood throughout the body.
- Heart Diseases- Buildup of fatty substances in blood vessels leads to atherosclerosis, impairing cardiac function. Fat accumulation may cause the heart to pump blood more rigorously, and when it fails, the blood gets collected in parts of the body, like the lungs, legs, or feet.
With weight reduction, a person is at a lower risk of these diseases and discomfort associated with managing excess body weight and can enjoy a healthier and fuller life.
Bariatric Surgeries to Treat Obesity
Bariatric Surgeries aim to treat class III obesity, also known as morbid obesity. People with a BMI of 40 or more, or 35 or more in people with any co-morbidity fall under class III obesity. Though weight reduction is not a one-time solution or a quick fix to obesity, proper diet checks, regular exercise, and positive lifestyle changes help achieve it sustainably.
- Gastric Sleeve Surgery- Known as Sleeve Gastrectomy, the surgery reduces the stomach size by approx. 80%, thus leaving behind a tubular sleeve that is banana-shaped. The reduced stomach size makes one feel fuller with less food intake. The surgery also reduces the amount of hunger hormones the stomach produces, thus restricting the impulses to eat more.
- Gastric Bypass Surgery- Gastric Bypass Surgery is also known as Roux-en-Y surgery. It is common bariatric surgery and is performed when diet and exercise fail to reduce weight. The surgeon creates a small pouch from the stomach and staples it. The small pouch gets separated from the rest of the stomach. This new pouch becomes the functional portion of the stomach. The newly created pouch is attached to the lower part of the small intestine, bypassing the upper portion. The swallowed food will go to the small pouch of the stomach, and then directly to the lower portion of the small intestine. The new route bypasses a major part of the stomach, and the upper portion of the small intestine.
- Duodenal Switch Surgery- The combination of Gastric Sleeve and Intestinal Bypass surgeries, this surgery removes a major portion of the stomach and attaches the smaller pouch to the lower intestine, creating a shorter path for the food to pass from the stomach to the intestine.
Bariatric Surgery -Lowering CVD Risks
By treating excess weight, the cause of CVDs, Bariatric Surgery lowers the future risk of these diseases. When excess weight is treated, the associated diseases are either prevented or eventually treated. When a person has to carry less weight, the heart has to put in less effort to pump blood and, hence, is at a lower risk of heart-related problems. For obese people already having CVD, studies show that those who had the surgery were at a lower risk of adverse outcomes than those with similar conditions who did not undergo the surgery. It reduces the incidence of heart failure, myocardial infarction, and stroke in obese patients. Without weight loss management or surgery, morbid obesity sooner or later leads to cardiovascular health issues. These chances could be reduced if one undergoes Bariatric Surgery. The surgery is a long-term treatment solution for weight loss and curtailing the associated health issues of high cholesterol, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, heart attack, stroke, and congestive heart failure.
Conclusion
Obesity is complex and chronic. It is not an aesthetic concern to be ashamed of or feel embarrassed about, but a medical concern that requires a proper line of treatment combined with a sustained diet plan, exercise routine, and positive lifestyle changes. Bariatric Surgery is the best long-term solution, safe and effective, with most patients experiencing losing excess weight, post-surgery. However, the outcome of each surgery varies and depends upon the post-operative care and weight management. The benefits outweigh the associated risks and complications that this surgery carries of a typical surgical procedure.
References
https://www.acc.org/Latest-in-Cardiology/Journal-Scans/2022/03/14/15/47/Bariatric-Surgery-and-CV-Disease
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/17285-bariatric-obesity-surgery
https://www.heart.org/en/news/2021/04/05/for-heart-patients-bariatric-surgery-may-lower-risk-of-future-cardiovascular-problems
https://www.acc.org/Latest-in-Cardiology/Journal-Scans/2022/03/14/15/47/Bariatric-Surgery-and-CV-Disease