Introduction
Motherhood is the most sacred feeling of every woman who brings and nurtures a new life with unconditional love. Women undergo transformative changes, not just emotionally or psychologically but physically as well, during and after pregnancy. Giving birth to a new life is a blessed moment for every woman and her near and dear ones. Still, one must not overlook the health concerns and complications often faced and experienced by them. These health issues could range from high blood pressure, gestational diabetes, excessive bleeding, anemia, and infection, including conditions like postpartum bodily changes, emotional stress and depression, fatigue, anxiety, or hernia.
Understanding the postpartum emotional, physical, and psychological health of women during and after pregnancy is of paramount importance for addressing the underlying causes and treating the symptoms of any such complications timely and adequate.
This blog discusses one such postpartum medical condition, hernia, along with its types, symptoms, and treatment for general awareness and information.
What is Postpartum Hernia?
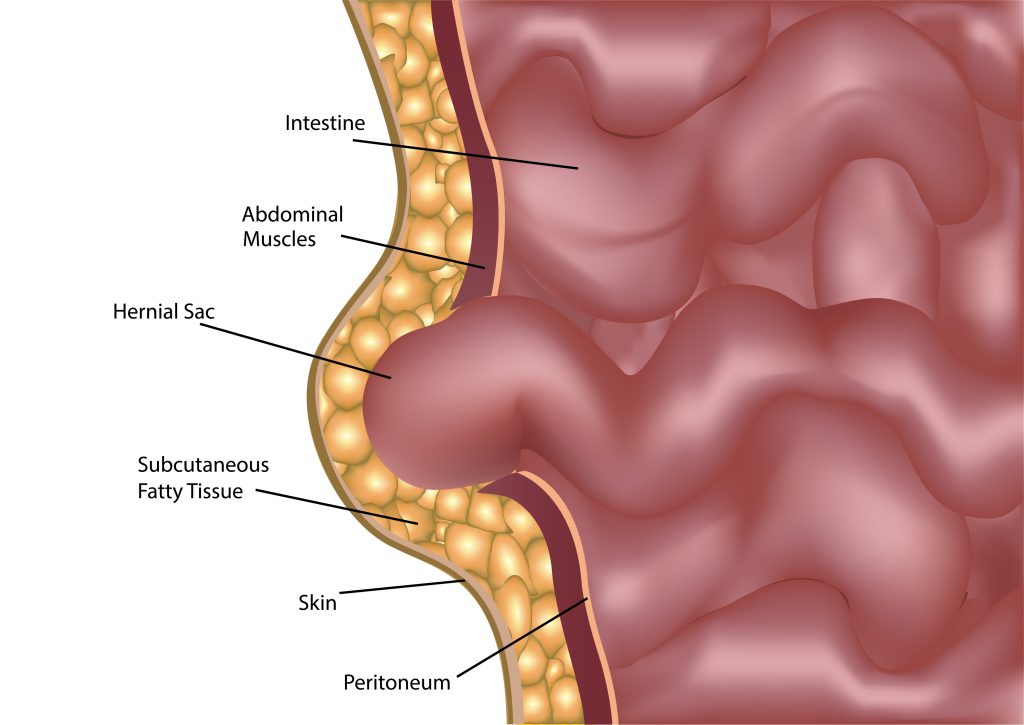
The term ‘postpartum’ refers to the medical condition of a woman after childbirth. Postpartum hernia is when the abdomen muscles get stretched due to weight gain, and a growing baby increases pressure on the abdominal wall. The belly fat, or the abdomen’s interior, pushes against the weak muscles, or the belly button protrudes through the weak muscles. In short, any hernia post-delivery is known as a postpartum hernia.
Causes of Postpartum Hernia
Physical changes that result in weight gain or obesity, excessive pressure or fluid buildup in the abdomen, multiple pregnancies, the birth of twins or triplets, heavy coughing, and c-section surgery are some of the common causes of postpartum hernia.
Types of Postpartum Hernia
Hernia, post-delivery, could be of various types. These types include-
- Umbilical hernia- The fetus is connected to the mother in the womb through an umbilical cord. This cord passes through the opening in the baby’s abdomen, which generally closes after birth. However, when this umbilical cord does not close completely, it leaves a weak spot in the baby’s abdomen, which may lead to a hernia anytime in the future. These hernias are commonly seen in infants but are also seen in women when the spot where the umbilical cord detached at birth does not heal.
- Inguinal hernia- During pregnancy, there can be pressure near the groin. Inguinal hernia occurs when the abdomen or intestine tissue bulges out through the opening in the lower abdominal wall. Inguinal hernia is caused in the inguinal canal.
- Ventral hernia- Ventral hernia occurs above the belly button, in the middle of the stomach. Also known as incisional hernia, it occurs at the previous surgical incision site, as in the case of c-section surgery that is not healed. The tissue protrudes from the weakened part of the abdominal wall, resulting in a bulge.
Symptoms of postpartum hernia
Hernias cause pain and discomfort. Though not a severe medical condition, it must be treated properly to prevent its severity. Some of the common symptoms of postpartum hernia are-
- Pain in the abdomen
- Bulge in the abdominal area or near the c-section site
- Vomiting or constipation due to strangulation of hernia
- Tenderness in the abdominal area
- Heightened pain and bulge due to pressure, coughing, lifting, or any physical activity
Treatment for postpartum hernia
In cases of small or minor hernia with no discomfort or pain, there is no need for urgency for its treatment. One may wait for it to grow in size to be treated surgically or laparoscopically. In cases of severe discomfort and pain, hernia needs to be treated timely and properly. However, one may avoid postpartum hernia by observing specific precautionary measures of avoiding heavy lifting, rigorous exercise, or physical exertion, ensuring support to the abdomen in case of severe coughing or sneezing to reduce pressure. Postpartum workout for strengthening the core muscles also helps in preventing hernia occurrence. It may be noted that postpartum hernia is treated through open hernia surgery or laparoscopic procedure.
- Open surgery- In the case of open surgery, the surgeon cuts open the abdomen with a large incision to access the hernia site, pushes the hernia back to place, and closes the incision with stitches.
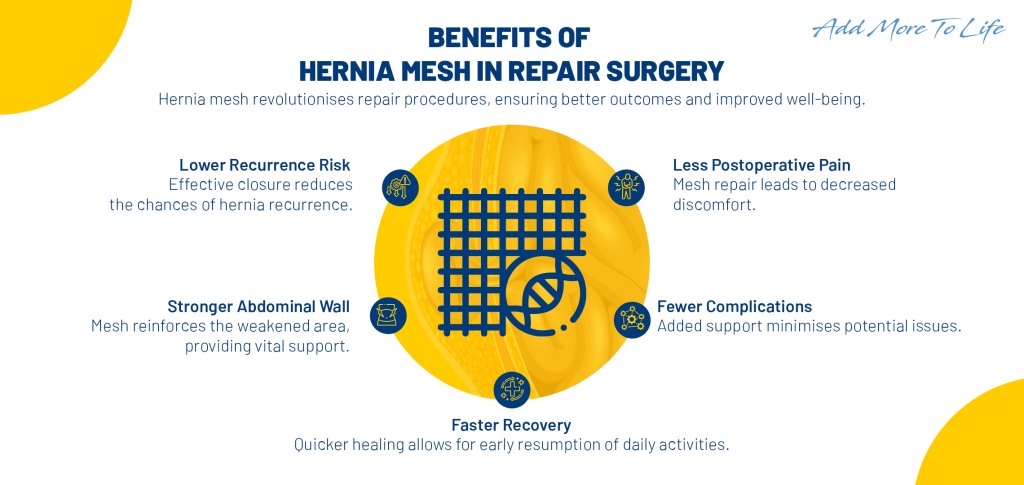
- Laparoscopic procedure- Also known as a keyhole procedure, the hernia is placed back into its position using tiny instruments inserted through smaller incisions on the abdomen. Once put in place, it is supported by a mesh attached to the surrounding tissues, thus reducing the chance of hernia reoccurrence. Hernia treatment involves pushing the protrusion back to its place and supporting it by placing a mesh.
The doctor often recommends using an abdominal binder (a wide belt worn around the abdomen) to support the treated hernia.
Recovery from hernia treatment requires nearly a few weeks of rest from physical activities that exert pressure on the abdomen.
Conclusion
Though hernias are not severe, they often become painful and cause discomfort if not treated promptly. Postpartum hernia can be prevented through adequate rest and avoiding activities that would exert pressure on the abdomen. The likelihood of hernia occurrence is high if one becomes pregnant again. Resorting to non-surgical techniques of workouts to strengthen the core muscles may help in preventing postpartum hernia. However, in cases of large and painful hernia symptoms, hernia repair is the only effective treatment option.