What is Laparoscopic Surgery?
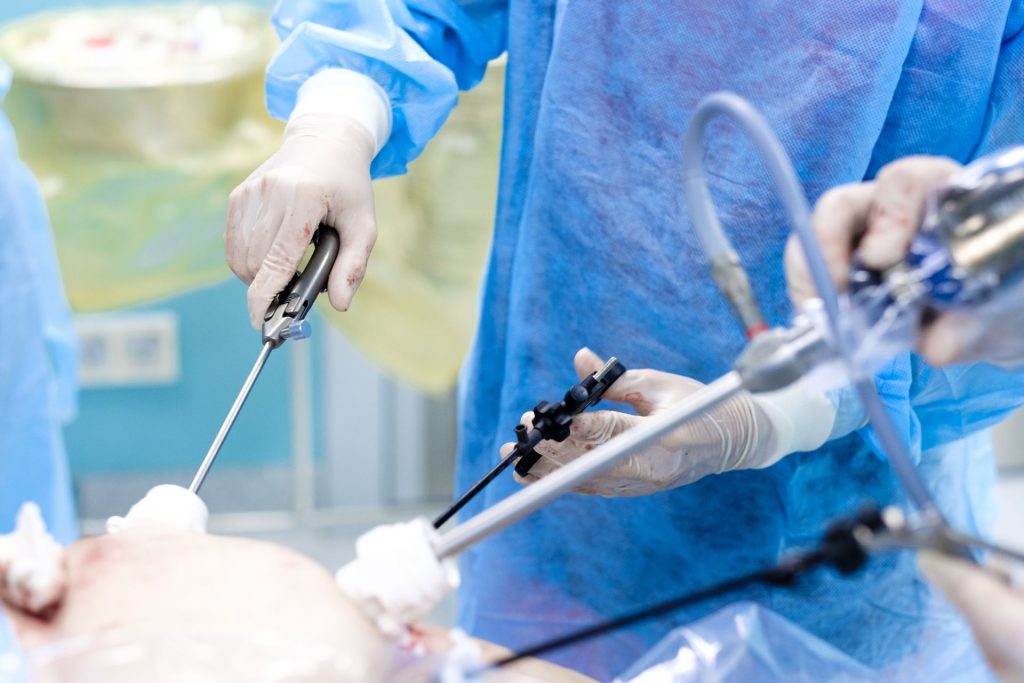
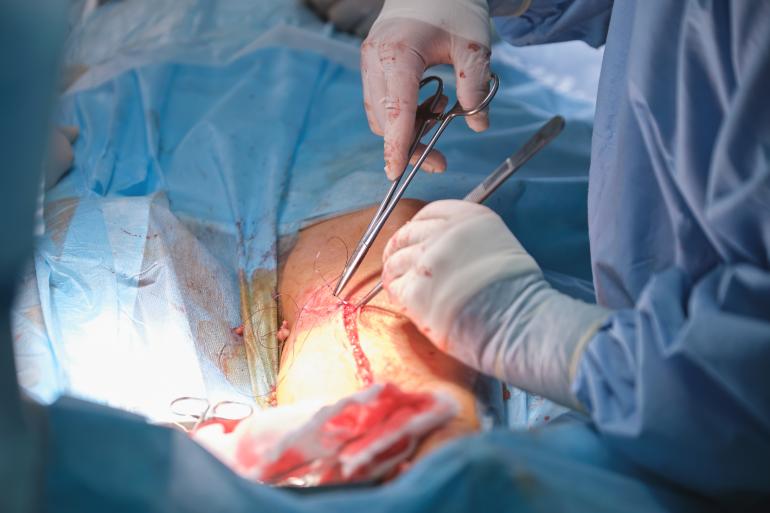
It is a minimally invasive surgical technique that allows doctors to perform surgeries through small incisions rather than large ones. The procedure involves using a laparoscope, a thin, long tube with a camera and light attached to it.
As part of the procedure, the laparoscope will be inserted through one of the incisions by the surgeon. The attached camera sends images to a monitor in the operating room. This allows the surgeon to see inside the patient’s body without making large incisions. The other ports will be used to insert small specialised instruments that the surgeon will use to manipulate and remove tissue.
Laparoscopic surgeries can perform a wide range of surgical procedures, including hernia repair, hysterectomy (uterus removal), appendectomy (appendix removal), and more.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgeries
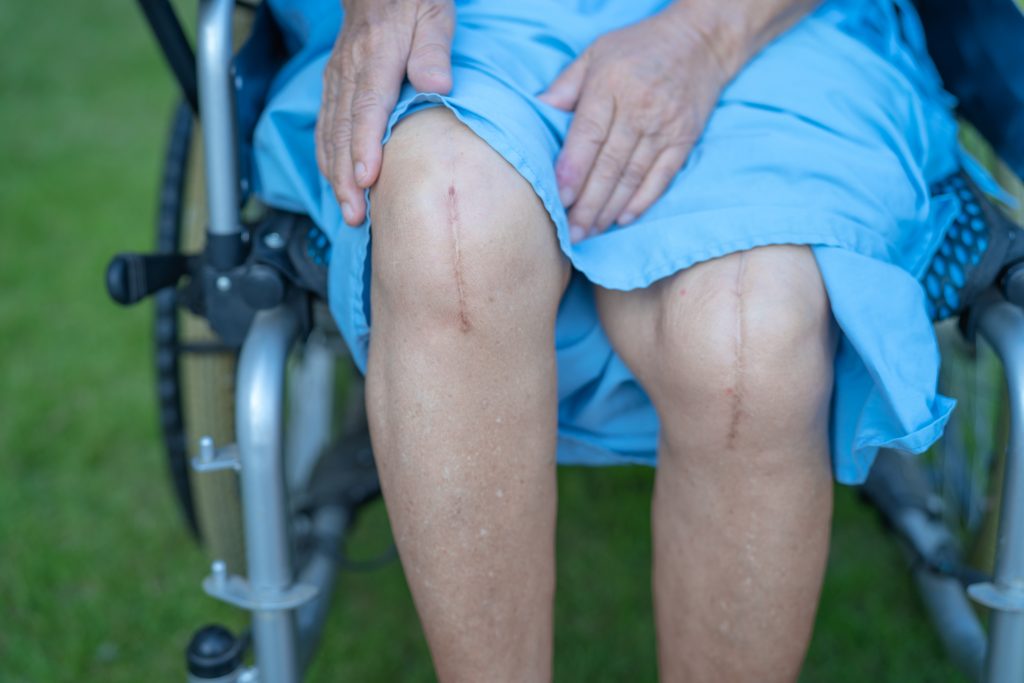
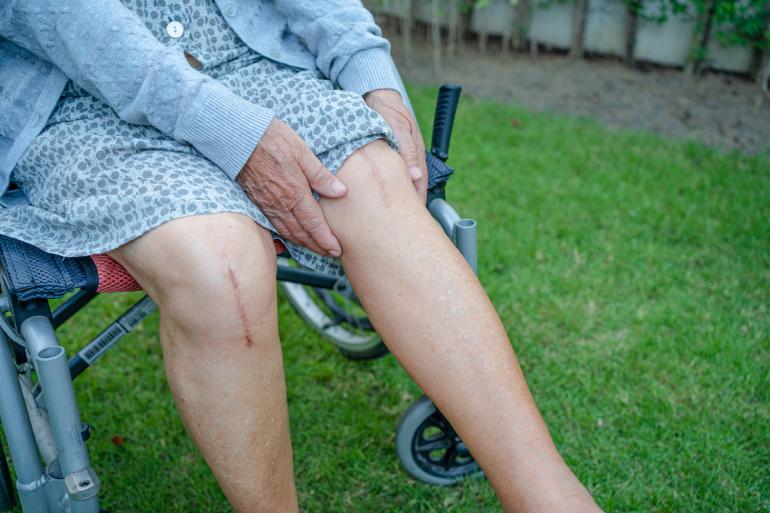
- Reduced pain and scarring: Compared to traditional open surgeries, laparoscopic surgeries cause less pain and scarring. This is because the incisions used for laparoscopic surgeries are smaller and require less cutting of the skin and tissue. Patients undergoing laparoscopic surgeries are less likely to need strong pain medications and will experience less discomfort during recovery.
- Faster recovery times and shorter hospital stays: Laparoscopic surgeries have shorter recovery times than traditional open surgeries. Patients who undergo laparoscopic surgeries can typically return to normal activities sooner and require less time in the hospital. This is because laparoscopic surgeries are less painful to the body, and patients experience less discomfort and inflammation.
- Lower risk of infection and other complications: Laparoscopic surgeries have a lower risk of infection and other complications than traditional open surgeries. This is because the small incisions used for laparoscopic surgeries are less likely to become infected, and there is less tissue trauma and blood loss during the procedure. This can also result in less scarring and better cosmetic outcomes.
- Reduced blood loss: Laparoscopic surgery often involves less bleeding than traditional open surgeries, reducing the need for blood transfusions. Insufflation is one of the key factors contributing to reduced blood loss in laparoscopic surgery, which involves filling the abdominal cavity with gas (usually carbon dioxide) to create space for the surgeon to work. By doing so, the gas pressure helps to constrict blood vessels and reduce bleeding during the surgery.
- Improved cosmetic outcomes: Laparoscopic surgeries result in better cosmetic outcomes than traditional open surgeries. The small incisions used for laparoscopic surgeries heal faster and leave minor scars, resulting in less visible scarring and improved cosmetic outcomes.
Conclusion
In recent years, laparoscopic surgeries have become a popular alternative to traditional surgeries, and for a good reason. These surgeries significantly benefit patients, making the entire surgical process more manageable and less painful. So, if you or someone you know requires surgery, talk to your healthcare provider about the possibility of laparoscopic surgery.
FAQs
Q: What is laparoscopic surgery, and how does it differ from traditional open surgery?
A: Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that uses small incisions and a camera to perform surgeries. It differs from traditional open surgery, which requires larger incisions and more tissue trauma.
Q: What types of surgeries can be performed using the laparoscopic approach?
A: Laparoscopic surgeries can be used to perform a wide range of surgical procedures, including hernia repair, hysterectomy (uterus removal), appendectomy (appendix removal), and more.
Q: What are the benefits of laparoscopic surgeries for patients?
A: The benefits of laparoscopic surgeries for patients include reduced pain and scarring, faster recovery times and shorter hospital stays, lower risk of infection and other complications, reduced blood loss, and improved cosmetic outcomes.
Q: What is the typical recovery time for laparoscopic surgery?
A: The recovery time for laparoscopic surgery depends on the type of surgery and the individual patient. However, generally, patients who undergo laparoscopic surgery have shorter recovery times than those who undergo traditional open surgery and can typically return to normal activities sooner.
References:
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/presentations/100166_1.htm
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/22552-laparoscopic-surgery
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/laparoscopy/#:~:text=Laparoscopy%20is%20a%20type%20of,surgery%20or%20minimally%20invasive%20surgery.
https://www.laparoscopyhospital.com/v1.htm
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2992667/