Planning a family is a big decision &, understandably, a few people may want to delay it at any given time. Over the years, this has been possible in large part due to the development of various contraception methods.
Your choice of birth control should depend on several factors including your health, frequency of sexual activity, number of sexual partners, and the desire to have children in the future.
There are different types of contraception:
- To prevent sperm from getting the eggs, contraception methods include condoms, diaphragms, cervical caps, and contraceptive sponges.
- Measures that keep the women’s ovaries from releasing eggs that can be fertilized include birth control pills, patches, shots, vaginal rings, and emergency contraceptive pills.
- Long terms measures for birth control include Intrauterine devices (IUD), intrauterine systems (IUS) that are implanted into the uterus. They can be kept in for several years
IUD is considered effective and safe for most women. They are also a long-lasting option. Let’s learn more about it.
What is an IUD?
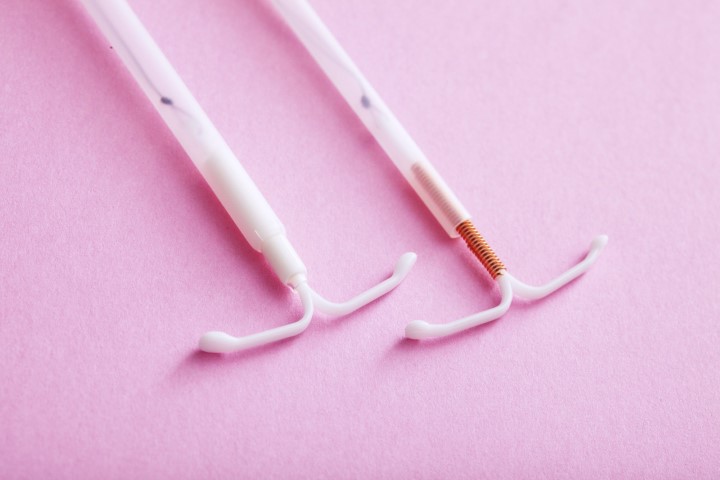
An IUD may be a small T-shaped plastic or copper device that’s inserted into the uterus by a doctor or nurse. Copper ions are released inside the uterus prevents pregnancy and protects for anywhere between 3 to 10 years. It is also called a ‘coil’ or ‘copper coil’. Unfortunately, there is a lot of misinformation regarding IUD that makes the patients apprehensive about the insertion.
IUDs aren’t the only form of birth control. An alternative to that is the Intrauterine System or IUS, which prevents pregnancy by releasing hormones in the uterus.
What is the difference between IUD and IUS?
Copper IUDs are made up of plastic frames with copper coil wound around them, IUS is made up of plastic frame which consists hormones. The main difference between IUD and IUS is that IUD releases Copper ions and IUS releases a hormone called progestogen and hormone Levernorgestrel (LNG). But unlike any other contraceptive pills or hormone contraception, the hormones in IUS are local which means they only work around the area of your uterus. This means they are likely to have an impact on your mood or cause any other physical symptoms which usually occur in other hormonal contraception.
A few facts about IUD
- It can be placed at any time during your menstrual cycle.
- When inserted correctly it can be 99% effective.
- It works as soon as it is inserted and lasts for between 3-10 years.
- It can be taken out whenever you want by a trained nurse or doctor.
- Your periods can be heavier, longer or more painful for 3 to 6 months after inserting in an IUD. Spotting or bleeding in between periods is also possible.
How does it work?
An IUD releases copper ions in the uterus which alters the cervical mucus, hence making it more difficult for sperm to reach the egg and survive. The copper ions released by the IUDs also work as a spermicide. It can also help a fertilized egg from being able to implant itself. Most healthy women can use an IUD. Women who are allergic to copper cannot use copper IUDs. They’re especially suited to women with one partner and at low risk of contracting an STD. IUDs don’t protect against STDs.
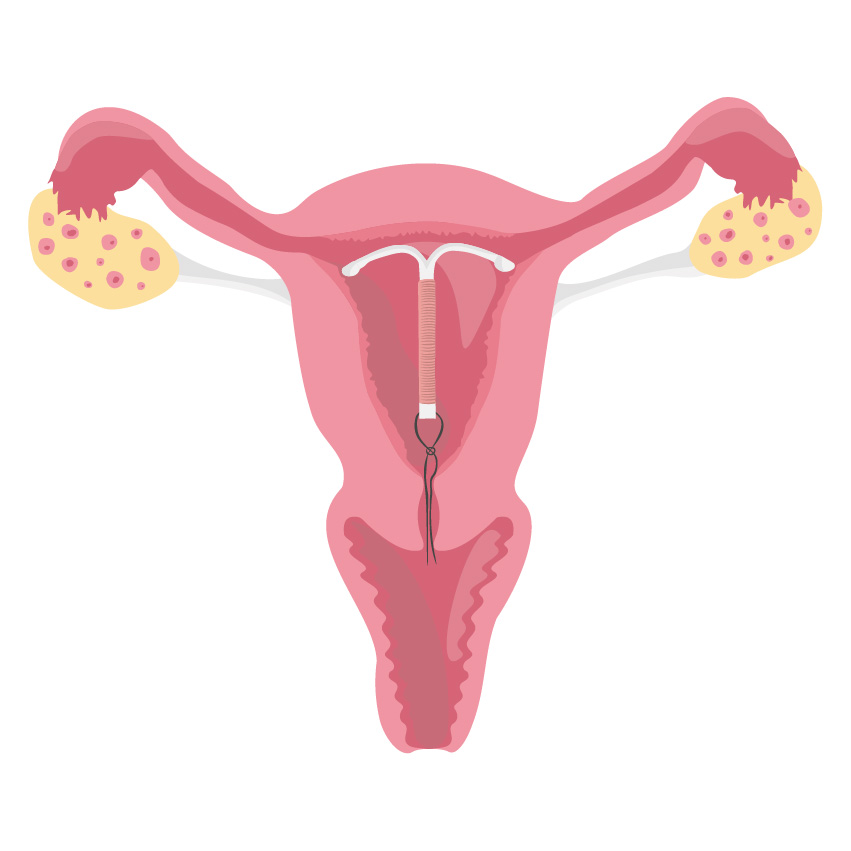


Benefits of IUDs
- They last for a long time.
- Mostly hassle-free, once inserted you or your partner don’t have to think about it.
- Safe to use even while you are breastfeeding.
- Cost-effective.
- There are no hormonal side effects such as acne, headaches, or breast tenderness.
- It is not affected by other medicines.
- Does not cause obstacles to intercourse.
- There is no evidence that an IUD will make you gain/lose weight or increase the risk of cervical cancer, womb cancer, or ovarian cancer.
How is an IUD inserted?
The IUD procedure takes place during a woman’s menstrual cycle (Secretary phase of the menstrual cycle). Before the procedure, a GP or nurse will check inside the vagina to understand the size and position of the womb uterus. Doctors may also test for infections such as STIs and give antibiotic medicines accordingly. After the examinations are done, the doctor will insert the IUD through the cervix and into the uterus. The entire procedure takes around 20-30 minutes to complete.
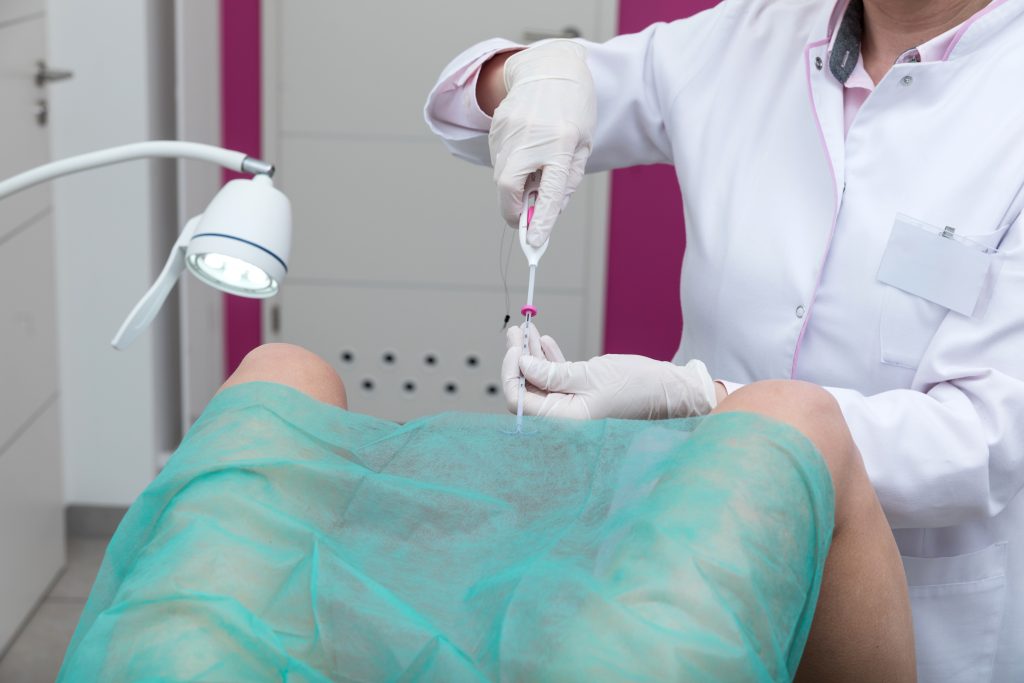


Is IUD insertion going to be painful?
The IUD insertion procedure depends from person to person. A few women may experience pain during the procedure. Your doctor knows what is best for you & may give an anesthetic or painkiller before they place the IUD. A few women may experience symptoms like cramps or bleeding once it is done. Post fitting, it is advisable to visit a GP after 3-6 weeks to make sure everything is okay.
While an IUD procedure is pretty common, it is always in your best interest to know about issues that may occur after it. Some of these include –
- Heavier, painful, or longer periods. This may improve in few months.
- Probability of Pelvic Infection
- An IUD doesn’t offer protection from STDs.
Most of the above-mentioned side effects are extremely uncommon and if one does feel the need to use an IUD, it is advisable to consult your healthcare professional and find out if the contraceptive method is correct for you.