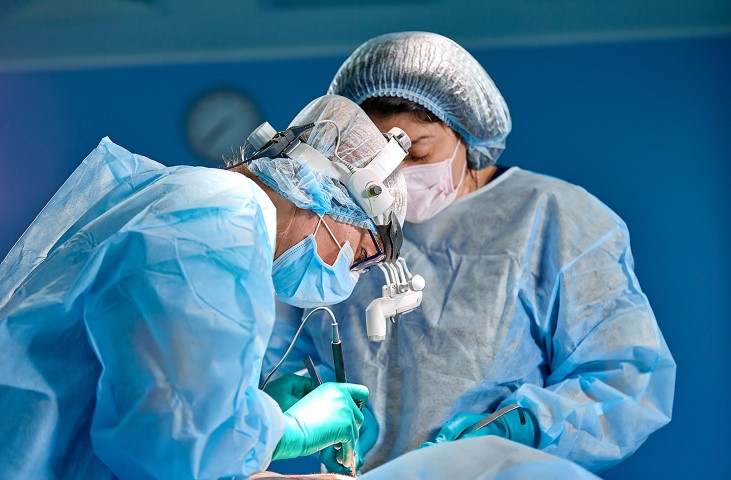
Apart from being an extremely vital organ, the heart is also a complicated one! Over the years, we have learned a lot about matters of the heart and many ailments can now be treated medically. One such ailment is Aortic Stenosis.
So, what is Degenerative Aortic Valve Disease?
Degenerative Aortic Valve Disease, also known as Degenerative Aortic Stenosis, is usually found among patients who are above 60 years of age. It is one of the most common cardiac diseases after hypertension and coronary heart disease.
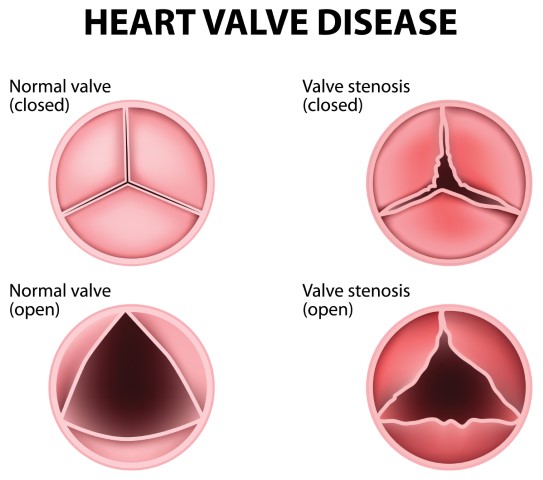


Degenerative Aortic Valve Disease, also known as DAVD, is a condition in which the left ventricle (the main pumping chamber in the heart) and the aorta don’t work properly, leading to complications. It is most prevalent in older people with a tricuspid valve, though younger people with a bicuspid valve are also susceptible to it. There are two types of Aortic Valve Diseases:
Aortic Valve Stenosis: In this condition, the cusps (leaflets) of the aortic valve become thick and stiff, which leads to the narrowing of the valve opening. This in turn blocks or restricts the flow of blood from the heart to the rest of your body.
Aortic Valve Regurgitation: In this condition, the valve doesn’t close properly, causing the blood to flow back to the left ventricle, which may prevent the heart from efficiently pumping blood to the rest of your body.
The Symptoms of Aortic Valve Disease may be mild or may not be experienced for many years. Some of the most common symptoms are:
- Abnormal heart sound
- Gasping and shortness of breath
- Fainting
- Tightness in the chest
- Extreme fatigue
- Arrhythmia (Irregular heartbeat)
What causes Degenerative Aortic Valve Disease?
The heart has four valves that aid in the blood flow. Each valve has a flap that opens or closes during every heartbeat. In Degenerative Aortic Valve Disease, the valve between the left ventricle and the main artery doesn’t work properly. The valve may either not open fully, blocking the blood flow from the heart to the body (stenosis), or the valve may not close properly, causing the blood to flow backward (regurgitation).
Aortic valve disease may be caused due to a heart defect present from birth, or due to other factors such as age, high blood pressure, infection/injury to the heart.
Risk Factors of Degenerative Aortic Valve Disease
Old Age: As mentioned before, Degenerative Aortic Valve Disease is more prevalent in older people as compared to young people.
Congenital Heart disease: If you had certain heart conditions at birth, the chances of getting Degenerative Aortic Valve Disease increases.
Infection: If you have had a history of infections in the heart, it may act as an impending factor.
Radiation Therapy: If you have undergone radiation therapy to the chest area, you are prone to Aortic Valve Disease.
Endocarditis: It is an inflammation in the heart’s inner lining involving heart valves, which in turn can turn into a major risk factor.
What are the complications involved in Degenerative Aortic Valve Disease?
While we now know about the various risk factors, we need to be mindful of the various ways the ailment can affect us. These include –
- Heart Failure: Aortic Valve Disease may lead to heart attack or cardiac arrest, which in turn will lead to heart failure
- Stroke: Patients who have Aortic Valve Disease are susceptible to stroke
- Blood clots: When diagnosed with Degenerative Heart Disease, there is a high risk of blood clots in the heart valves.
- Arrhythmia: Abnormal heartbeat is a very common symptom of DAVD
- Death: If not treated properly, on time, Aortic Valve Disease may cause malfunctioning of the heart, leading to certain death.
Can Degenerative Aortic Valve Disease be diagnosed?
After discussing the signs and symptoms with your doctor, he/she may review your medical history and even conduct a physical examination. After the physical examination, your doctor may prescribe certain tests to diagnose your condition.
Echocardiogram: This test uses sound waves to provide images of your heart to evaluate the chambers, aortic valve, and blood flow.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): Electrodes are attached to your skin to measure your heart activity. An ECG can deduct enlarged heart chambers, abnormal rhythms, and other conditions.
X-ray: A chest x-ray can help determine if the heart is enlarged and it also helps doctors examine your lung condition.
Cardiac CT scan: A CT scan uses multiple x-rays to create a detailed image of your heart and valves.
Can Degenerative Aortic Valve Disease Be Treated?
The treatment for degenerative aortic valve disease depends on the severity of your condition. Once you have been thoroughly evaluated, your doctor will discuss with you to provide the right treatment. Some common treatment options are:
Aortic Valve Repair: To repair the aortic valve, surgery needs to be conducted to either separate valve cusps that have fused, removing excess valve tissues, or patching holes in the valves. If diagnosed with Aortic Stenosis, the doctor might conduct a procedure to insert a catheter with a balloon into an artery via the groin and move it towards the aortic valve. The balloon inserted is inflated to expand the valve. Once the valve is expanded, the balloon is deflated, and the catheter is removed.
Aortic Valve Replacement: This is one of the most sought-after measures to treat DAVD. In Aortic Valve Replacement, the surgeon removes the damaged valve and replaces it with a new valve. The new valve can either be a mechanical valve, or a valve made from cow, pig, or human heart tissue. This is usually done with open-heart surgery also known as Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement.
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: TAVR is a minimally invasive method to treat a narrowed aortic valve that fails to open properly. It is performed on patients after thorough consultation from their doctors. In this procedure, the doctor inserts a catheter through the blood vessel in the leg or chest lining and guides it to the heart to relieve the problem of aortic valve stenosis.
Degenerative Aortic Valve Disease is among the common cardiac diseases, which, if left untreated, can become fatal. While seeking out treatment options, consult with your doctor about which treatment procedure would work best for you. It is also important to weigh the pros and cons of each option before going ahead with the treatment. You can also talk to your doctor about the lifestyle changes you can make to overcome the complications and ensure that the condition doesn’t relapse.