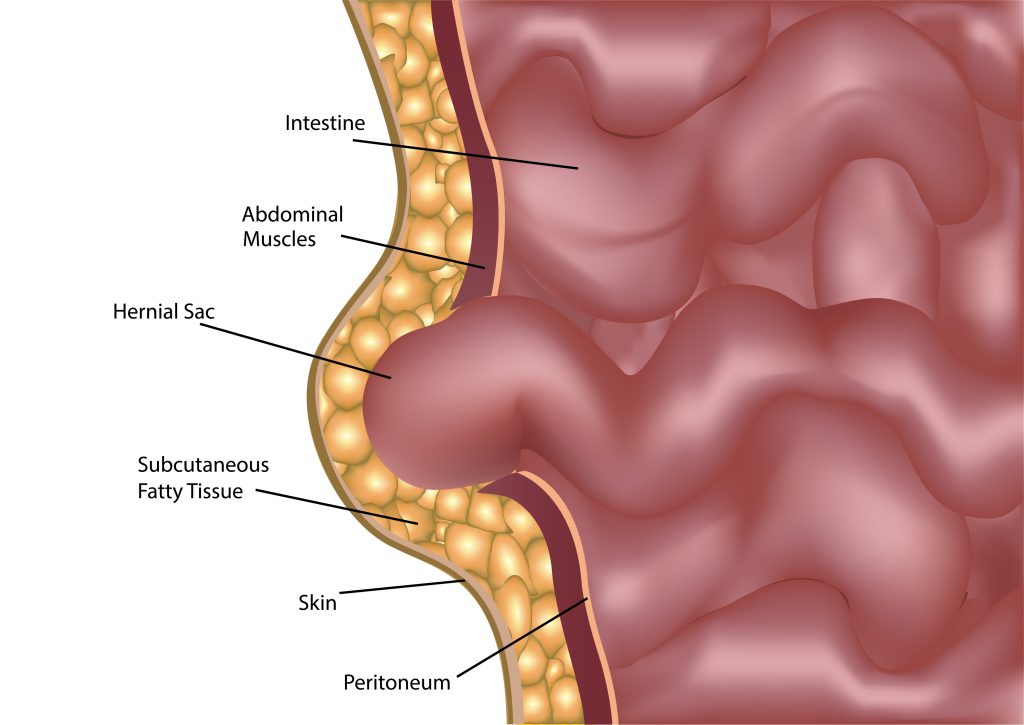
Hernias are more common than you might think, and knowing what type you have is key to getting the right treatment. Whether you’re experiencing discomfort or just curious about hernias, understanding the difference between inguinal and femoral hernias is essential. These two types of hernias often occur in the groin area but differ in their specific locations and symptoms. Our article provides a clear understanding of both these hernias and what to expect if you or a loved one needs hernia surgery.
What is Inguinal Hernia?
An inguinal hernia occurs when tissue, such as part of the intestine, protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles. This type of hernia is located in the groin area, specifically at the inguinal canal. The inguinal canal, in simple terms, is a passage in the lower abdominal wall. The inguinal canal, in men, carries the spermatic cord and, in women, contains the round ligament of the uterus.
Types of Inguinal Hernias
There are two types of inguinal hernias: direct and indirect.
Direct Inguinal Hernia: Occurs when the hernia pushes through a weak spot in the fascia of the abdominal wall and enters the inguinal canal directly. It typically occurs in older adults due to the weakening of the abdominal muscles over time.
Indirect Inguinal Hernia: Follows the pathway that the testicles made during pre-birth development, i.e. descending from the abdomen into the scrotum. Indirect inguinal hernias are more common in younger individuals.
What is a Femoral Hernia?
A femoral hernia occurs when tissue pushes through the wall of the femoral canal, which is located just below the inguinal ligament near the upper thigh. This type of hernia is less common than an inguinal hernia but can be more serious.
Differences Between Inguinal Hernia and Femoral Hernia
The anatomical difference between femoral and inguinal hernias is the location of the hernia. Inguinal hernias are located in the inguinal canal in the groin, while femoral hernias occur in the femoral canal near the upper thigh. This distinction is important for diagnosis and treatment.
Common Causes for Inguinal and Femoral Hernias
Both inguinal and femoral hernias can be caused by similar factors, including:
Heavy Lifting: Straining the abdominal muscles can lead to hernias.
Chronic Coughing: Persistent coughing increases pressure on the abdominal wall.
Obesity: Excess weight puts additional strain on the abdominal muscles.
Pregnancy: The increased pressure on the abdomen during pregnancy can lead to hernias.
Differences in Risk Factors
While the causes are often similar, there are some differences in risk factors.
- Inguinal hernias are more common in men due to the structure of the male groin area.
- Femoral hernias, on the other hand, are more common in women, especially those who are older or have had multiple pregnancies.
Comparison of Symptoms
The symptoms of inguinal and femoral hernias can vary but often include:
- Inguinal Hernia Symptoms: A noticeable bulge in the groin area, pain or discomfort in the groin, especially when bending over or lifting, and a heavy or dragging sensation in the groin.
- Femoral Hernia Symptoms: A bulge near the upper thigh or groin, pain or discomfort in the upper thigh, and severe pain if the hernia becomes incarcerated or strangulated.
Diagnostic Process
Diagnosing both types of hernias typically involves a physical examination where a doctor looks for a bulge in the groin area. Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may be used to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for inguinal and femoral hernias are similar. Both often require surgical interventions, especially if they are at risk of complications. Hernia surgeries can be performed using open surgery or laparoscopic surgery.
Wrapping It Up
Understanding the differences between inguinal and femoral hernias is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. While both types of hernias occur in the groin area, their anatomical locations and risk factors differ. If you suspect you have a hernia, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Reference Links:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/inguinal-hernia/symptoms-causes/syc-20351547
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16266-inguinal-hernia