Have you ever heard someone say that only men get hernias? Or that all hernias need surgery? These are just a couple of the many myths floating around about hernias. It’s easy to be misled by misinformation, especially when it comes to health. Understanding the facts about hernias can make a significant difference in how we approach prevention and treatment. Let’s clear up these common misconceptions.
Myth 1: Hernias Only Occur in Men
Clarification and Facts: While it is true that men are more likely to develop certain types of hernias, such as inguinal hernias, women and children are not immune to this condition. Hernias can occur in anyone, regardless of gender or age. For instance, umbilical hernias are more common in infants and pregnant women, while femoral hernias tend to occur more frequently in women owing to the wider shape of the female pelvis.
Myth 2: All Hernias Require Surgery
Explanation: Not all hernias require immediate surgical intervention. The decision to undergo surgery depends on multiple factors like the size and location of the hernia, symptoms, and complications. Some small and asymptomatic hernias can be monitored through a watchful waiting approach. However, surgery becomes necessary if there is a risk of complications such as strangulation, where the blood supply to the herniated tissue is cut off, or incarceration, where the hernia becomes trapped and cannot be pushed back in.
Myth 3: Hernias Are Always Painful
Variability of Symptoms: Hernia pain can vary greatly in intensity, from mild discomfort to severe pain. It depends on the type and severity of the hernia.
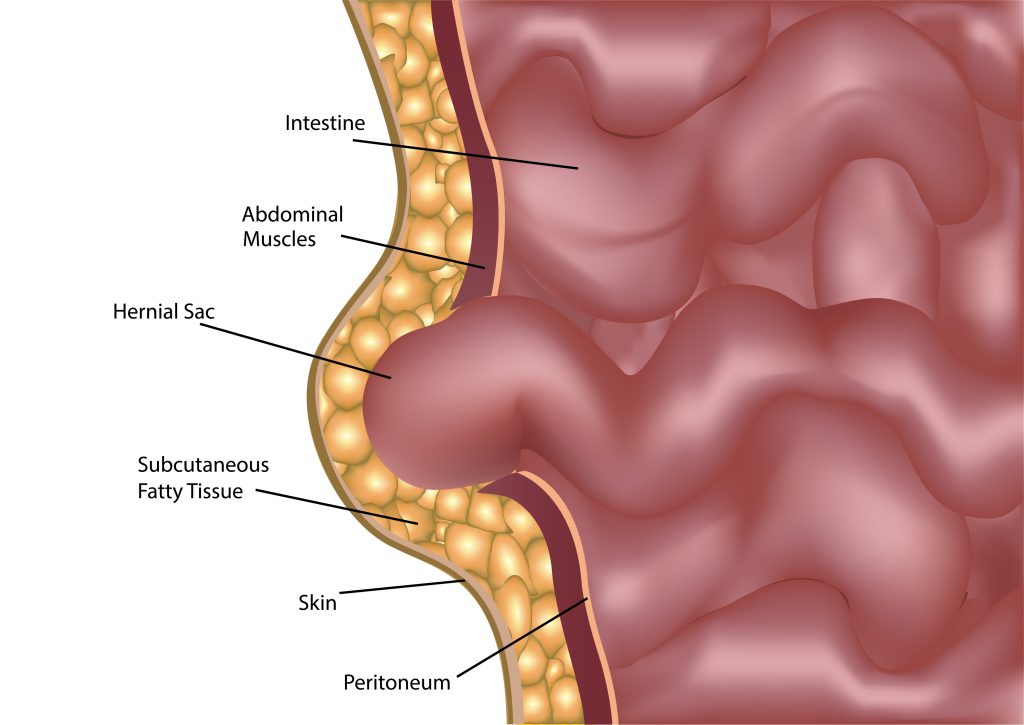
Symptoms to Watch For: Apart from pain, other symptoms of a hernia include a visible bulge in the affected area, heaviness or pressure, and discomfort that worsens with activities such as lifting, bending, or coughing. Look out for these signs and seek medical advice if you suspect a hernia.
Myth 4: You Can Push a Hernia Back In Yourself
Risks of Self-Treatment: Attempting to push a hernia back in manually can be dangerous and is not recommended. This practice, known as reduction, can lead to serious complications.
Recommended Action: If you suspect you have a hernia, it is crucial to seek medical attention. A healthcare provider can perform a proper evaluation and recommend a suitable treatment plan.
Myth 5: A Truss or Belt Can Cure a Hernia
Effectiveness and Limitations: While trusses and belts may provide temporary relief from the symptoms of a hernia, they do not address the underlying cause. These devices work by applying pressure to the hernia, which can help reduce discomfort and prevent the hernia from protruding. However, they do not offer a permanent solution and should not be relied upon as a cure.
Medical Advice: Before using any supportive devices, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider.
Myth 6: Exercising With a Hernia Is Safe
Safe vs. Unsafe Activities: Exercising with a hernia can be safe, but it is important to choose the right activities. Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, and yoga can be beneficial without putting excessive strain on the hernia[6]. However, high-impact activities and exercises that involve heavy lifting or intense abdominal strain should be avoided.
Preventive Measures: When exercising with a hernia, it is crucial to listen to your body and avoid any movements that cause discomfort.
Myth 7: Hernias Are Caused Solely by Heavy Lifting
Broader Causes: While heavy lifting is a common cause of hernias, it is not the only factor. Other causes include chronic cough, obesity, and conditions that increase abdominal pressure, such as constipation and pregnancy[1]. Hernias can also result from a combination of these factors.
Risk Reduction Strategies: To reduce the risk of developing a hernia, it is important to maintain a healthy weight, practice proper lifting techniques, avoid smoking (to reduce chronic cough), and ensure a balanced diet rich in fibre to prevent constipation. Additionally, engaging in regular exercise to strengthen the core muscles can help support the abdominal wall.
Conclusion
Understanding the facts about hernias is crucial in managing and preventing this condition effectively. By debunking these common myths, we hope to provide you with a clearer understanding of hernias and the importance of seeking appropriate medical advice.
Reference Links:
[1] https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15757-hernia
[2] https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/umbilical-hernia/symptoms-causes/syc-20378685
[3] https://www.parents.com/pregnancy/my-body/aches-pains/pregnancy-symptoms-complaints-umbilical-hernia/#:~:text=Umbilical%20hernias%20are%20a%20common,during%20pregnancy%20or%20after%20delivery.
[4] https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/femoral-hernia-repair/#:~:text=It%20pushes%20through%20a%20weak,hernias%20are%20rare%20in%20children.
[5] https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320888#:~:text=A%20strangulated%20hernia%20occurs%20when,Any%20hernia%20can%20become%20strangulated.
[6] https://www.nghs.com/2021/04/12/can-i-exercise-when-i-have-a-hernia
[7] https://ketteringhealth.org/5-tips-for-preventing-a-hernia/




Comments are closed.