Sutures Used in Dentistry for Periodontal Surgery
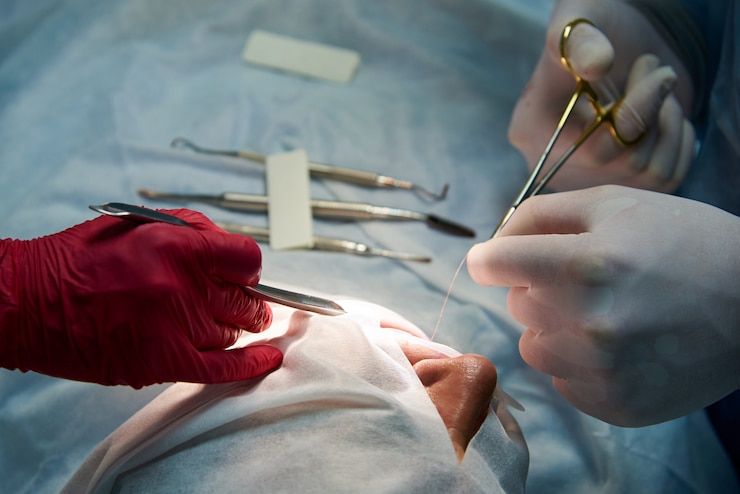
Periodontal surgery in dentistry means preventing or correcting anatomical, developmental, traumatic, or plaque-related defects in the teeth and Gums. The periodontal gums are tissues that surround the teeth. These tissues help form the base of the tooth and support it. If the gums get damaged or diseased, you may need periodontal surgery. This involves removing a small portion of gum tissue to relieve pain or correct an issue with your gums. Dental suturing provides strength and integrity to the decayed tissue post-surgery and controls bleeding. It is essential to understand different types of periodontal sutures used in dental surgery as each work differently and has its pros and cons. It is also essential to understand what kind of surgery you are undergoing to know which type of suture is right for you.
What is a Suture?
A suture is a material, primarily a type of thread used extensively and commonly in all kinds of surgery as a tissue closure. When a suture is used in periodontal surgery, it is used to close the gap between two teeth. Sometimes, doctors may use sutures to correct gum disease or relieve pain. The most common sutures used in dental surgery are Polypropylene, Polyglactin 910, Silk and Polyglactin 910 Antibacterial.
Types of Sutures based on the material composition
Polypropylene : These are made from Polypropylene monofilament and are very strong yet soft, making them suitable for various periodontal surgeries.
Polyglactin 910 & Polyglactin 910 with Antibacterial : These are made from Polyglactin 910, a synthetic absorbable material with excellent Histocompatibility with the Gum tissues. These can be also be had with Antibacterial properties
Silk : Non absorbable braided, coated suture made from natural silk filaments widely used across dental surgeries
Properties of good Sutures
Selecting the right suture depends on the anatomical structure and the area where surgery is to be performed, as much as the surgeon’s technique and experience. The properties of an ideal suture are
- Durability – is the quality of a suture’s strength or ability to withstand stress.
- Tensile Strength – is the amount of force needed to stretch a suture. Minimum tension force should be applied to the suture to enable wound closure.
- Elasticity – is the degree to which a suture can be stretched without being torn and the ability to return to its original form and length after the stretch.
- Knot Security – Is related to the suture knot not getting slipped once the surgeon has placed on the tissue
- Minimal Tissue Reaction – A good suture should resist the bacterial growth and cause minimal reaction in the tissue post implantation
Suturing Techniques used in Periodontal Surgery
Simple Interrupted Technique : It is the most common suture technique where the suture passes from one side of the wound and exits on the other, with a knot on top.
Risks in Periodontal Surgery
The risks associated with periodontal surgery are-
- Graft Infection – This is where infection occurs in the grafted area. The chances of this happening are low, but it is still a risk.
- Wound Infection – This happens when an infection occurs in the surgical wound. The chances of this happening are high.
- Bleeding – This happens when the suture tears during surgery or the surgical site ooze blood.
- Pain – This is usually associated with surgery and caused by the cut tissue.
Advantages of Sutures Used in Periodontal Surgery
The advantages of sutures used in periodontal surgery are-
- Quick Recovery – When compared to other types of surgery, oral surgeries have less recovery time because the muscles are not damaged.
- No Reassessment Needed for Wound Care – Most oral surgeries require the patient to be reassessed for wound care, but sutures do not.
- No Oral Surgery for Jaw Fusion – Oral surgeries such as extraction of teeth and periodontal surgery do not require a fusion of the jaw, making a recovery faster as less time is spent in the hospital.
- No Oral Surgery for Orthodontic Treatment – Periodontal surgery can be performed on non-adherent gums, whereas extractions are usually performed on adherent gums. This makes recovery quicker as less time is spent in the hospital.
Conclusion
Periodontal or gum surgery is a surgical procedure in which the inflamed and septic Gums are treated by grafting healthy gums from the oral gum tissues. The most common periodontal surgeries are gum re-habilitation, gingival augmentation, and gum grafting. Due to the risk of infection, gum re- habilitation and gum grafting are the only two gums surgeries that need to be performed in a sterile environment. The patient’s gums are often too damaged to re- habilitate or graft them. In this case, a re-habilitation may be performed to help the patient eat soft foods again.



Comments are closed.