Introduction
When prioritizing health, we make room for a healthy beginning for healthy living ahead. Each problem has a solution, and overweight or obesity is no exception. Obesity is one of the common ailments and is on a constant upward trend in India and globally. Reports show that in India, nearly 100 bariatric surgeries are performed daily, with the year 2022 reporting about 39,949 surgeries.
With high emergence cases of obesity and overweight cases, medical professionals expect and recommend the need for effective measures to curtail them. These measures include non-surgical treatment options to start with and subsequent surgical intervention if the former does not yield the desired results.
Bariatric Surgery, the most effective and successful treatment for obesity and weight loss, is in much demand. Understanding the purpose, types, and advantages of this surgery helps patients and their caregivers form an informed decision while deciding the course of treatment for addressing the problem of obesity and weight loss. A detailed discussion in this blog serves this specific purpose.
What is Bariatric Surgery?
Bariatric Surgery is, also known as weight loss or metabolic surgery, performed to treat obesity and weight loss through surgical intervention. The surgeon resizes the stomach and intestinal tract of the patient to restrict food intake and nutrient absorption in the body. Surgery, along with treating obesity, also helps treat diabetes, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and other related health problems through diet control when accompanied by healthy lifestyle habits and physical activity.
Types of Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric Surgery comes with various options depending on the needs of individual cases. Each has its benefits and potential shortcomings. The different types of Bariatric Surgery are-
- Gastric Sleeve Surgery- This sleeve gastrectomy creates a banana-sized and shaped functional portion of the stomach. Nearly 80% of the stomach portion is removed. Reducing the stomach’s capacity to hold food and fluid affects the body’s metabolism. It reduces hunger-producing hormones and provides the fullness of the stomach with less food. It is a simple procedure and hence safe and does not involve any complications of intestinal bypass. However, the surgery is non-reversible.
- Gastric Bypass Surgery- Gastric Bypass Surgery is called Roux-en-Y surgery, which means ‘in the form of a Y’. The surgery reduces the stomach into a small egg-sized pouch. The surgeon staples the small, pouched stomach, separating it from the rest of the stomach. The small intestine is also divided. The lower portion of the small intestine is brought up and connected to the newly created stomach pouch. The bypassed stomach and upper portion of the small intestine are attached further down the small intestine. This creates a ‘Y shape’. The food passes from the new pouch to the small intestine for digestion, bypassing the major portion of the stomach and the upper portion of the small intestine. The modified course of the digestive tract enables less food consumption, fullness experience, and reduced nutrient absorption. The patients can have effective and long-lasting solutions for weight reduction when accompanied by healthy lifestyle changes, physical activity, and doctor-recommended weight control and management. It is considered the gold standard for weight reduction. It has long-lasting weight loss results if accompanied by proper weight control and management.
- Duodenal Switch Surgery- Duodenal Switch surgery combines Gastric Sleeve and Gastric Bypass surgeries. The stomach is reduced to a banana size and shape after removing nearly 80% of the stomach portion. The newly created sleeve-shaped portion is attached to the lower portion of the small intestine, thus bypassing its upper portion. The food passes directly from the newly created stomach to the small intestine’s lower portion. This results in less food consumption and less nutrient absorption. It is a highly effective treatment for obesity and type 2 diabetes. It creates high malabsorption and possibilities of vitamin and mineral deficiencies post-surgery that need to be addressed through nutrient supplements.
Who is a Good Candidate for Bariatric Surgery?
The surgery is recommended for people who-
- Have body mass index (BMI) >40, or
- Have a BMI >35 but <40 with comorbidities like type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, or heart problems, or
- Are 45 kgs more than the ideal body weight (when BMI is between 18.5 to 24.9).
Advantages of Bariatric Surgery
This surgery offers many benefits, the foremost being weight loss to treat obesity. The others on the list are-
- Improves cardiovascular health with the control of high cholesterol, blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes, enabling the control of heart diseases like heart stroke, myocardial infarction, and peripheral vascular diseases.
- Relieves depression by treating obesity, one of the causes of anxiety, stress, and social, emotional, and physical embarrassment in obese people.
- Relieves joint pain and eliminates chances of knee joint replacement by reducing excess weight on joints.
- Prevents other medical conditions like the risk of miscarriage in women, pregnancy complications, gall bladder disease, and other metabolic syndrome.
What to Expect in Bariatric Surgery
Pre-surgery evaluation for patients
Bariatric Surgery could be a life-changing procedure that helps patients achieve weight loss, treat obesity, and enable healthy living with overall well-being, with proper diet and weight loss control and management.
For the successful outcomes of the surgery and better patient care, it is crucial to identify the barriers that need to be addressed and post-operative instructions to be followed. A multidisciplinary team of experts does a preoperative evaluation to rule out the chances of complications and adverse surgical results in patients.
Preoperative evaluation focuses on the issues unique to the patient. The evaluation includes:
- The patient’s medical history.
- Physical examination.
- Various tests for psychological, psychosocial, behavioral, nutritional, and anatomical assessment.
Each assessment evaluates a specific aspect of the patient to ensure effective risk management, surgical performance, and efficient patient care.
Preoperative requirements
The patient who qualifies for the surgery needs to –
- Commit to the doctor’s recommended diet plan. This may require a reduction in calorie consumption, the type of food intake, and quitting smoking and alcohol.
- Exercise and perform physical activity as part of the doctor-recommended health plan.
- Either continue or stop medications as advised by the doctor.
- Stay positive and participate in preoperative education and counseling sessions, if any, provided by their healthcare providers.
- Explore and discuss the various surgical options and stay informed about the risks, benefits, and complications to make an informed decision.
- Gather information about the cost of the surgery, hospital stay, insurance coverage, and other incidental medical expenses.
During the surgery
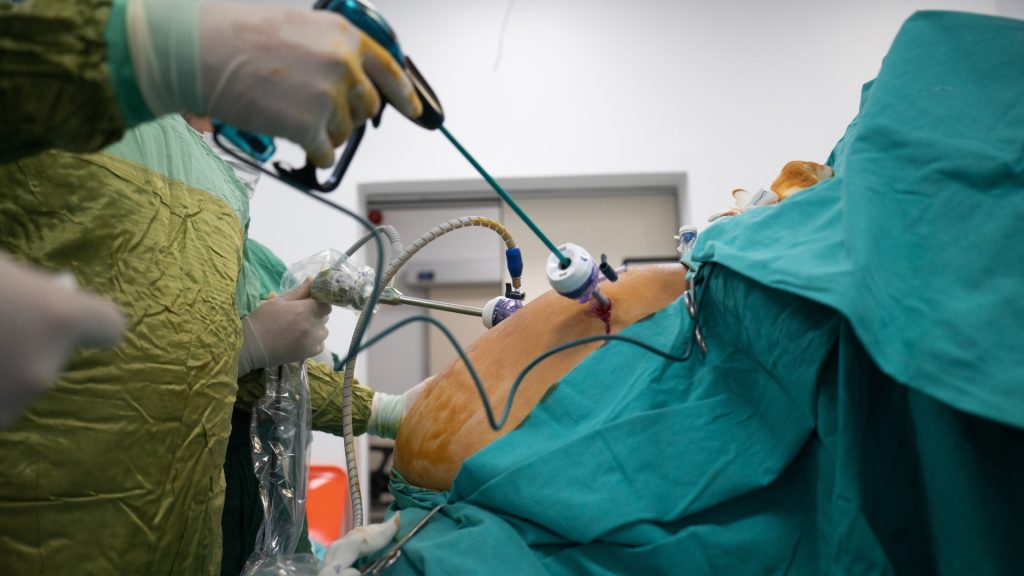
The patient is put under general anesthesia, and the surgery may be done traditionally or laparoscopically. The duration of the surgery depends on the type and method of surgery.
In the case of traditional surgery, there is a large incision on the abdomen to gain access to the surgical site. While under laparoscopic surgery, small incisions are made. A laparoscope with a tiny camera attached to its tip is inserted through the incision. The camera enables the surgeon to view and operate through a small incision. The healing and recovery depend on the method, with laparoscopic surgery providing faster healing and recovery compared to traditional.
Post-operative care
After a few days of post-operative hospital stay, the patient is discharged with doctor-prescribed medications, pain control, and management guidelines. Weight loss is not a one-time fix but requires regular follow-up visits with the doctor, monitoring the weight changes, and reporting the same to the doctor if severe. A controlled diet, routine exercise, healthy lifestyle, stress management, and patient commitment to adhere to the same consistently is a must.
Conclusion
Bariatric Surgery is a healthy beginning towards achieving desired weight loss goals and treating obesity, the root cause of various cardiovascular diseases. India is preferred for Bariatric Surgery for its low operative cost, prompt and timely medical attention, and intervention by expert and qualified professionals.
Although the most effective weight loss treatment, Bariatric Surgery needs post-surgical constant and consistent patient commitment, regular checks, and diet control, accompanied by routine physical activity, positive lifestyle changes, and stress management to make it a long-term success story with desired results.
References
https://asmbs.org/patients/bariatric-surgery-procedures
https://health.clevelandclinic.org/7-bariatric-surgery-benefits-besides-helping-you-lose-weight/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK594256/#:~:text=The%20preoperative%20assessment%20helps%20identify,and%20improves%20weight%20loss%20outcomes.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/bariatric-surgery/about/pac-20394258
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/bariatric-surgery/about/pac-20394258


Comments are closed.