Overview
We have all heard about a loved one or a friend suffering from a sudden cardiac arrest, commonly known as a heart attack. But what exactly is a heart attack and how does it affect people? The answers to the questions are things that everyone needs to know about.
What is a heart attack?
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) also called Heart diseases are a group of disorders of the heart and blood vessels. The root causes of cardiovascular diseases is atherosclerosis (blockages in coronary arteries), a process mainly governed by lifestyle factors.
A heart attack also called a myocardial infarction occurs when the flow of the blood towards the heart is blocked, mostly due to the accumulation of fat, cholesterol, or other substances. This build-up results in the formation of plaque in the coronary arteries, ones that feed the heart. The plaque can form a blood clot which leads to interrupted blood flow thus damaging the heart muscles. This eventually leads to a heart attack.
How do you spot an oncoming heart attack?
A heart attack can be fatal depending on the severity of the attack. Heart attack symptoms can vary from person to person ranging from mild to severe. Some people may get a sudden heart attack whereas some may experience symptoms a few days or months in advance. Continuous and recurring chest-pain is the most recognizable symptom, and it is advised to seek medical assistance if the pain persists over a long duration. But there are a few symptoms that are easy to spot. These include:
- Feeling of tightening, pressure, and pain in the chest
- Difficulty in breathing
- Fatigue
- Cold Sweat
- Abdominal problems- indigestion, heartburn or stomach pain
- Nausea
- Dizziness
Other than this, the heart attack symptoms in men specifically include chest pain, chest discomfort or pressure, or shortness of breath. The heart attack symptoms in women include pressure or squeezing in the center of the chest, shortness of breath, and nausea.
What are the factors that cause a heart attack?
So far, we have learned how to spot a heart attack. But, it is essential to know the factors that lead up to it.
The main heart attack cause is the blockage of coronary arteries that result in a build-up of fatty substances. This forms plaque that may rupture and spills substances like cholesterol in the bloodstream, hampering the flow of the blood. A clot forms at the place of the rupture that blocks the blood flow in the coronary arteries making it impossible for the oxygen and nutrients to reach the heart. This condition is also called Ischemia. Such coronary artery disease causes heart failures.
There are two types of blockage/heart attacks you must know:
- Partial Blockage- NSTEMI (non-ST elevation myocardial infarction): A less serious form of heart attack, the coronary arteries are partially or temporarily blocked. Proper medication and evaluation are required to diagnose this condition.
- Complete blockage- STEMI (ST-elevation myocardial infarction): This is a form of heart attack that completely blocks the coronary artery resulting in a large part of heart muscle deprived of blood flow.
Am I at risk of getting a heart attack?
People of a certain age group and pre-existing conditions are at a higher risk of falling prey to a heart attack. These include:
- Age: Women above the age of 55 and men above the age of 45 are more prone to a heart attack as compared to younger people.
- Blood Pressure: High blood pressure damage your arteries increasing the change of blood pressure. Pre-existing conditions like obesity, diabetes, or cholesterol can worsen the situation and make you more likely to have a heart attack.
- High Cholesterol levels or Triglyceride levels: There is an increased risk of heart attack if your body has high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol or high levels of triglycerides (a type of blood fat).
- Diabetes: If your body is unable to produce insulin- the hormone secreted by the pancreas results in increased blood sugar levels in the body which in turn causes the risk of a heart attack.
- Family history: If you have a family history of heart attacks, it increases the risk of heart disease.
- Preeclampsia: A heart attack symptom in women is preeclampsia- a risk condition that causes high blood pressure in women during pregnancy. If any woman has a history of this condition, she is prone to heart attacks for a lifetime.
- Other risk factors to consider: decreased physical activity, obesity, tobacco consumption, drugs, stress.
How do the doctors diagnose a heart attack?


If you are showing any heart attack symptoms you should be immediately admitted to a hospital. Firstly, your blood pressure, temperature, and pulse will be checked followed by you getting admitted to a heart-care unit. You will be connected to a heart monitor to diagnose your condition. There are varied tests done for diagnosis:
- ECG (Electrocardiogram): A process done within the initial minutes of admitting the patient, an ECG test measures the electrical activity of your heart. It is a painless test that involves flat metal discs also called electrodes attached to your chest, arms, and legs. These electrodes have wires that are connected to the ECG machine that display the electrical impulses on the monitor or gets printed on the paper. This helps the doctor to know whether you are going through a heart attack.
- Other tests are done for the diagnosis of a Heart attack: Blood tests to check leakage of proteins in your blood, chest x-ray, Echocardiogram (graphic outline of heart’s movement), Coronary angiography (detection of blockages in the coronary arteries), MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), etc.
What happens to a person during a heart attack?



Various complications can occur from a heart attack. Some people may experience a mild heart attack with no serious complications. Some may experience a major heart attack with varied grave complications. Following are some of the other complications that are commonly faced by people:
- Arrhythmia: This includes irregular or abnormal heartbeats- beating too quickly, beating too slowly, or beating irregularly. A heart attack damages the heart muscles disrupting the electrical circuits that control the heart leading to Arrhythmia. Some arrhythmia causes mild symptoms such as dizziness, palpitations, or chest pain. However, some arrhythmia can be life-threatening and can result in death.
- Heart Failure: When your heart is not able to pump blood to your body effectively, it results in heart failure. There are times when a heart attack damages heart tissues extensively leading to the inefficient working of muscles. The intensity of the condition depends on the situation and can be treated with proper medications or surgery.
- Cardiac Shock: A cardiogenic shock leads to a sudden stopping of the heart without any warning. If the heart attack causes extreme damage to the heart muscles, your heart can no longer pump enough blood required for the functioning of the body, as a result causing this complication.
- Heart Rupture: A serious complication – heart rupture refers to the splitting or rupturing of the heart’s muscles or walls. Usually, open-heart surgery is recommended.
What are the treatments involved?
The heart attack pain can become worse sometimes. Depending upon the situation, medical or surgical treatment is suggested by the doctor. A few treatments are as follows:
- Oxygen Therapy: Oxygen therapy is kind of a treatment where extra oxygen is supplied to the body via nasal cannula, face mask, or a small tube inserted into your windpipe. This helps the body to work well.
- Medicines such as Beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, Anticlotting medicines, Aspirin, etc. are given to maintain heart health or to reduce the risk of another heart attack. They are often prescribed to prevent first or recurrent stroke.
- Thrombolytics: These drugs, also called clot busters, help dissolve a blood clot that’s blocking blood flow to your heart. The earlier you receive a thrombolytic drug after a heart attack, the greater the chance you’ll survive and have less heart damage.
- PCI – Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Also known as coronary angioplasty and stenting, in this treatment, the doctors insert a long, thin tube or catheter via an artery in your groin or wrist to widen the blocked coronary artery.
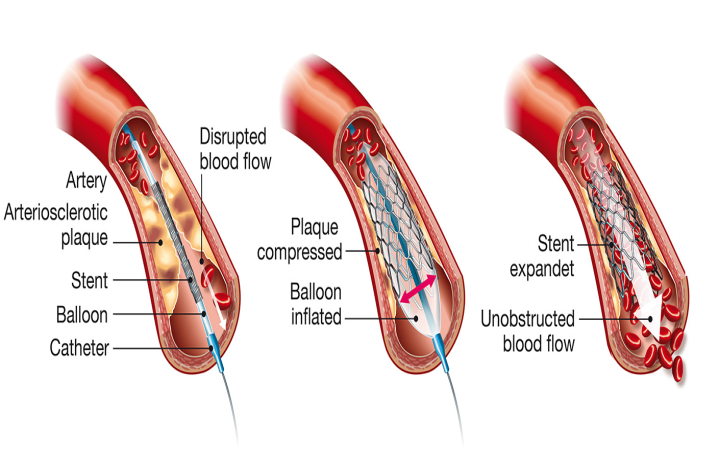


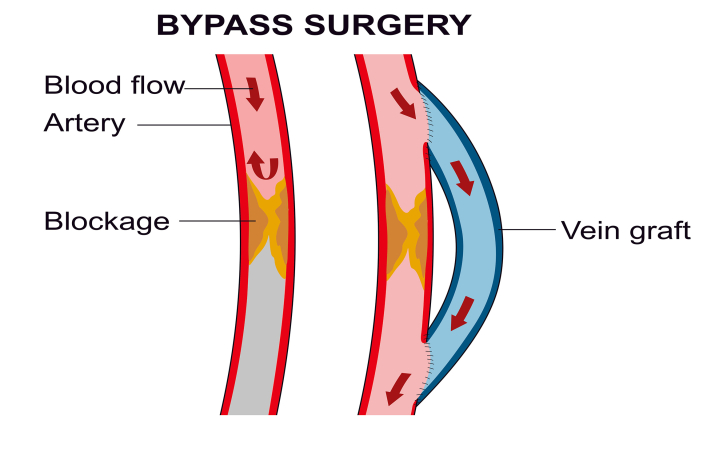
- Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery: This surgery is mostly done in emergencies, at the time of heart attack. The bypass surgery involves taking a blood vessel from another part of the body and attaching it to a place beyond a blocked coronary artery to improve the blood flow.


How do I stay clear of a heart attack?
Prevention is always better than cure. Take preventive steps to avoid having a heart attack or even another heart attack. Resorting to a healthy lifestyle is a paramount heart attack prevention measure to avoid heart attack as well as its complications.
- A healthy, balanced diet and lifestyle: Improve the health of your heart by maintaining a healthy weight, avoid smoking and drinking, exercise regularly. Managing stress by indulging in yoga and focusing on yourself helps in heart attack prevention. Control conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol by consulting a doctor.
- Medical Monitoring: Consult a doctor and monitor your heart condition regularly especially if you have pre-existing conditions like high blood pressure or high levels of cholesterol. Take medications that can reduce the risk of heart attack and help your heart to work efficiently.
Post-Surgery care
After a heart attack, the condition of the heart tissues and muscles continuously deteriorate. Hence, it is very important to undergo immediate heart attack treatment.
The doctor will assess your situation and recommend the medications. You must stick to the routine set by your doctor so that you can steer clear of relapse or any additional complications.
To conclude, a heart attack can be a traumatic experience, but if you maintain a balanced lifestyle and keep an eye out for symptoms, you can stay clear of it. If a person does show the signs that they are getting a heart attack, it is important to immediately reach out to a doctor and seek medical assistance. Even if it isn’t a heart attack, it is always best to be completely sure and safe!